Concepts
LeaderWorkerSet (LWS)
An LWS creates a group of pods based on two different templates (the leader template and the worker template), and controls their lifecycle.
Conceptual Diagram
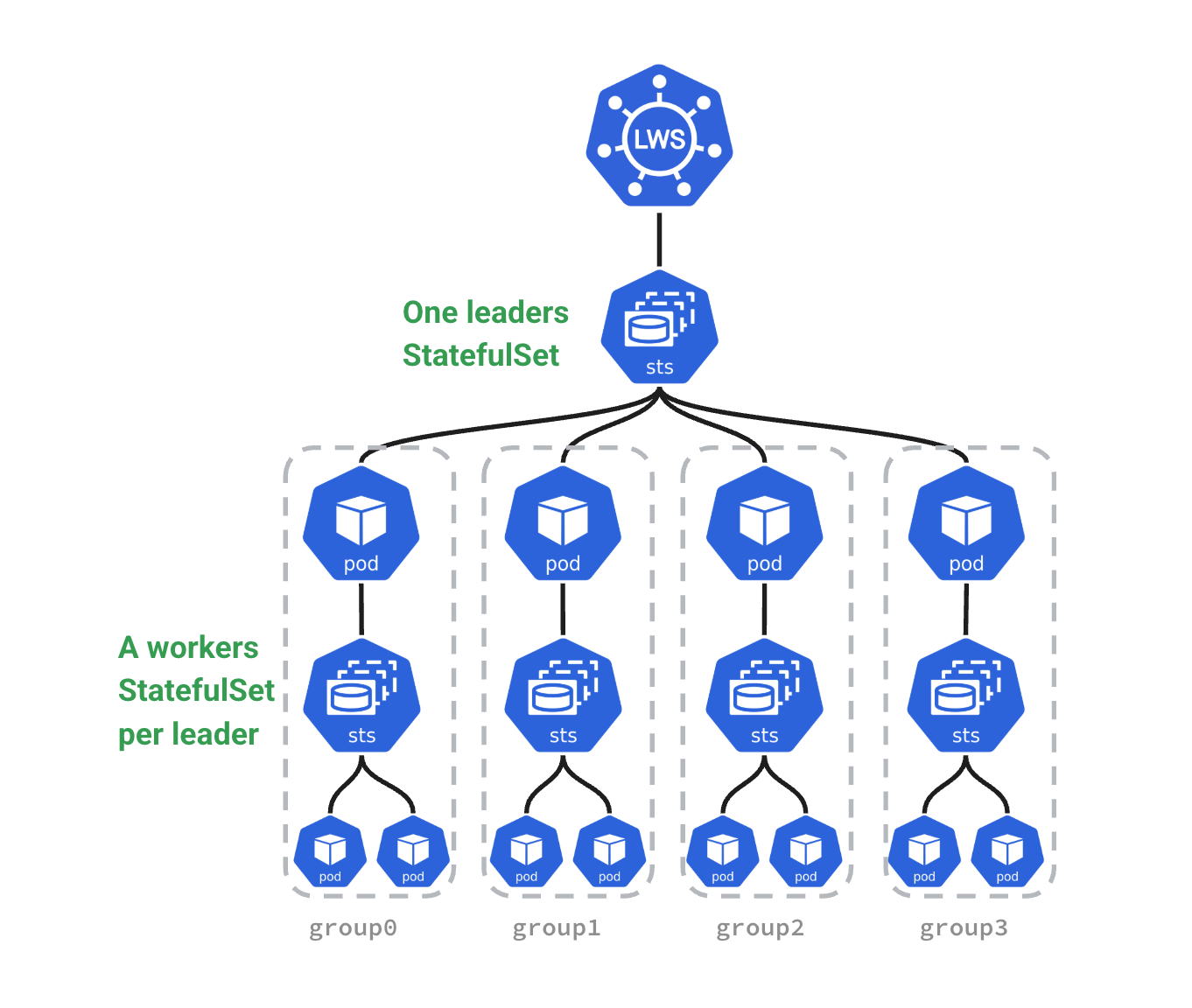
Running an Example LeaderWorkerSet
Here is an example LeaderWorkerSet
apiVersion: leaderworkerset.x-k8s.io/v1
kind: LeaderWorkerSet
metadata:
name: leaderworkerset-sample
spec:
replicas: 3
leaderWorkerTemplate:
size: 4
workerTemplate:
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginxinc/nginx-unprivileged:1.27
resources:
limits:
cpu: "100m"
requests:
cpu: "50m"
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
To list all the pods that belong to a LWS, you can use a command like this:
kubectl get pods --selector=leaderworkerset.sigs.k8s.io/name=leaderworkerset-sample
The output should be similar to
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
leaderworkerset-sample-0 1/1 Running 0 6m10s
leaderworkerset-sample-0-1 1/1 Running 0 6m10s
leaderworkerset-sample-0-2 1/1 Running 0 6m10s
leaderworkerset-sample-0-3 1/1 Running 0 6m10s
leaderworkerset-sample-1 1/1 Running 0 6m10s
leaderworkerset-sample-1-1 1/1 Running 0 6m10s
leaderworkerset-sample-1-2 1/1 Running 0 6m10s
leaderworkerset-sample-1-3 1/1 Running 0 6m10s
leaderworkerset-sample-2 1/1 Running 0 6m10s
leaderworkerset-sample-2-1 1/1 Running 0 6m10s
leaderworkerset-sample-2-2 1/1 Running 0 6m10s
leaderworkerset-sample-2-3 1/1 Running 0 6m10s
Multi-Template for Pods
LWS support using different templates for leader and worker pods, if a leaderTemplate field is specified. If it isn’t, the template used for
workerTemplate will apply to both leader and worker pods.
apiVersion: leaderworkerset.x-k8s.io/v1
kind: LeaderWorkerSet
metadata:
name: leaderworkerset-sample
spec:
replicas: 3
leaderWorkerTemplate:
size: 4
leaderTemplate:
spec:
workerTemplate:
spec:
Startup Policy
.spec.startupPolicy controls when the worker StatefulSet is created relative to its leader Pod. There are two options:
LeaderCreated(default): The LWS controller creates the worker StatefulSet as soon as the leader Pod object is created. This does not guarantee any readiness order between the leader and workers.LeaderReady: The LWS controller delays creating the worker StatefulSet until the leader Pod isReady.
apiVersion: leaderworkerset.x-k8s.io/v1
kind: LeaderWorkerSet
metadata:
name: leaderworkerset-sample
spec:
startupPolicy: LeaderReady
replicas: 3
leaderWorkerTemplate:
...
Exclusive LWS to Topology Placement
The LWS annotation leaderworkerset.sigs.k8s.io/exclusive-topology defines a 1:1 LWS replica to topology placement. For example,
you want an LWS replica to be scheduled on the same rack in order to maximize cross-node communication for distributed inference. This
can be done as follows:
apiVersion: leaderworkerset.x-k8s.io/v1
kind: LeaderWorkerSet
metadata:
name: leaderworkerset-sample
annotations:
leaderworkerset.sigs.k8s.io/exclusive-topology: rack
spec:
replicas: 3
leaderWorkerTemplate:
...
Subgroup
A SubGroup represents a logical subdivision of Pods within a workload. While LWS as a whole ensures that Pods in a workload can be scheduled as a group, SubGroups are useful when only part of the workload needs to be scheduled together. This lets you define smaller scheduling units within the larger workload group, which is helpful when subsets of Pods have tighter coordination requirements.
For example, in disaggregated serving, one SubGroup could represent prefill servers and another could represent decode servers. Each Pod within a SubGroup might need to be scheduled on the same rack for performance, but it is less critical if different SubGroups are placed on separate racks. However, you still want related SubGroups (e.g., prefill and decode servers) to remain in the same zone to minimize latency.
SubGroup Size
The size of a SubGroup determines how many Pods it contains. For example, if a prefill server requires 8 Pods to operate together, you can define a SubGroup of size 8. The scheduler ensures that all 8 Pods are considered together when making placement decisions. This prevents partial scheduling that could cause the workload to hang or waste resources.
SubGroupType: LeaderOnly
The LeaderOnly type means that a SubGroup is created exclusively for the leader. Workers are placed into separate subgroups according to the configured size, rather than being included with the leader.
This ensures that leader pods remain isolated in their own subgroup, while workers are organized independently.
This enables heterogeneous scheduling — for example, placing the leader Pod on CPU nodes while placing all worker Pods on GPU nodes, with exclusive placement to ensure they land on the same GPU rack.
For more details, see:
Exclusive Placement
The LWS annotation leaderworkerset.sigs.k8s.io/subgroup-exclusive-topology defines a 1:1 between an LWS subgroup to topology placement. This can
be useful for dissagregated serving in order to place the prefill pod group in the same rack, but on a separate rack from the decode pod group, assuming
same hardware requirements.
metadata:
name: leaderworkerset-sample
annotations:
leaderworkerset.sigs.k8s.io/subgroup-exclusive-topology: rack
spec:
replicas: 3
leaderWorkerTemplate:
subGroupPolicy:
subGroupSize: 2
size: 4
Volume Claim Templates support
LWS supports the use of volumeClaimTemplates for leader and worker pods, allowing the incorporation of storage class in volumeClaimTemplates to create persistent volumes in leader and worker pods. Below is an example demonstrating how to utilize volumeClaimTemplates in LWS.
apiVersion: leaderworkerset.x-k8s.io/v1
kind: LeaderWorkerSet
metadata:
name: lws
spec:
replicas: 2
leaderWorkerTemplate:
...
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: persistent-storage
spec:
storageClassName: default
accessModes: ["ReadWriteOnce"]
resources:
requests:
storage: 100Gi
leaderTemplate:
...
spec:
containers:
- name: leader
...
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /mnt/volume
name: persistent-storage
workerTemplate:
spec:
containers:
- name: worker
...
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /mnt/volume
name: persistent-storage
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.